NISP



INNOVATION AND START UP POLICY
FOR STUDENTS AND FACULTY MEMBERS, ALIGNED WITH NISP-2019
Galgotias College of Engineering & Technology, Greater Noida, Uttar Pradesh,
(An Autonomous Institute under UGC Act 1956, Approved by AICTE & affiliated to AKTU)
Knowledge Park I, Greater Noida, Uttar Pradesh 201310.
Website: https://galgotiacollege.edu//
ABSTRACT
Innovation and Startup Policy, GCET (ISP-GCET) has been formulated for students and faculty members of the GCET. The prime objective ISP-GCET is to develop an entrepreneurship and startup ecosystem powered by innovative minds with experiential learning. Thereby, the aim is to develop and foster a business ecosystem enabled by contemporary technology with high capacity of technological development and scalability as an essential component. ISP-GCET has envisioned becoming a world class technology driven innovation and incubation center at GCET, leading to entrepreneurship and startup. ISP-GCET is perfectly aligned with national innovation & startup policy-2019 and bound to empower the innovation, entrepreneurship & startup mission of India as a stakeholder.
Further, the prime objective is to provide a universal platform for research, innovation and development for the benefits of budding entrepreneurs, corporate houses & the society at large. It also elaborates Innovation Pipeline and Pathways for Entrepreneurs at Institute Level, Pedagogy and Learning Interventions for Entrepreneurship Development Collaboration. Institute participation in co-creation, Business Relationships and Knowledge Exchange is also discussed at sufficient length. Issue of Entrepreneurial Impact Assessment is also addressed in this policy along with the mention of annual felicitation day to motivate the students to opt entrepreneurship as a carrier option and to felicitate their proud parents. This policy is aligned with IPR policy of GCET, which mentions all the issues related to IP and Product Ownership Rights for Technologies Developed at Institute Organizational Capacity, and IEC policy of Galgotias Educational Institutions (GEI) which accounts and organize all the efforts being done by the institute for promoting and nurturing innovation based startup and entrepreneurship which was adopted as fourth pillar of the institute.
Contents
| Contents | Page No. | |
| i | About Institute | 3 |
| ii | About Galgotias Centre for Experiential Learning, Innovation and Incubation (GCELII) | 4 |
| iii | Preamble | 5 |
| iv | Vision and Mission | 6 |
| 1 | Strategies and Governance | 7 |
| 2 | Startups Enabling Institutional Infrastructure | 8 |
| 3 | Nurturing Innovations and Startups | 9 |
| 4 | IP and Product Ownership Rights for Technologies Developed at Institute | 10 |
| 5 | Organizational Capacity, Human Resources and Incentives | 10 |
| 6 | Creating Innovation Pipeline and Pathways for Entrepreneurs at Institute Level | 11 |
| 7 | Norms for Faculty Startup | 13 |
| 8 | Pedagogy and Learning Interventions for Entrepreneurship Development | 14 |
| 9 | Collaboration, Co-creation, Business Relationships and Knowledge Exchange | 15 |
| 10 | Entrepreneurial Impact Assessment | 16 |
| 11 | Review of the Policy | 17 |
| 12 | Way Forward | 17 |
i) About Galgotias Educational Institutions (GEI)
Galgotias Educational Institutions (GEI) have been inculcating practical skills and creating global professionals for more than two decades. Galgotias College of Engineering & Technology (GCET) under flagship of GEI, synergizes theoretical knowledge and practical skills to prepare professionals with highest competence. It was founded by Smt. Shakuntala Educational and Welfare Society, Galgotias Educational Institutions is currently led by Mr. Suneel Galgotia, Chairman and a resolute visionary. Galgotias College of Engineering & Technology is placed among the best in professional education in Dr. A.P.J Abdul Kalam Technical University (Formerly U.P. Technical University). The Galgotias Institute of Management & Technology and Galgotias College of Engineering & Technology are approved by AICTE, Ministry of HRD, Government of India and affiliated to Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam Technical University, Lucknow formerly Uttar Pradesh Technical University. It has achieved top positions in MBA, MCA and B. Tech and a record of 100% placements with the best corporate houses. It has also been ranked amongst the top engineering colleges in India by DATAQUEST NASSCOM survey and OUTLOOK-C Fore College Survey.
Galgotias Educational Institutions combine a supremely empowering educational process, industry stalwarts in their faculty, global educational associations and relentless placement efforts, to offer the best of career opportunities to its students. Galgotias Educational Institutions are known for a combination of state-of-the-art campus, strategic teaching-learning process, together with the most advanced facilities, creating an environment in which wholesome corporate personalities are created. GEI organizes several inter and intra-institute fests and runs value-based courses. It's been the Centre of Excellence in various aspects due to its contemporary high-tech labs and development of effectively elevating hobby clubs in various departments. The focus of the institute is to evolve as an innovative and achieve unique global standards of teaching-learning experience, R&D, quality placements and entrepreneurship.
ii) Galgotias Centre for Experiential Learning, Innovation and Incubation (GCELII)
In 2018, Govt. of India launched the Institution's Innovation Council (IIC) program through the Ministry of Education (MoE) Innovation Cell (MIC), for Higher Educational Institutions (HEIs), in collaboration with AICTE. In the month of November 2021, management established Galgotias Centre for Experiential Learning, Innovation and Incubation (GCELII) in the premises of Galgotias college of Engineering and Technology, Greater Noida. GCELII is a technology driven business incubator & Entrepreneurship (e)-Cell within the premises of GCET. GCELII is being run by a highly efficient multi-member board. It has been established with an objective of practicing innovation based on experiential learning, to inculcate excellence within Technocrats, Researchers and Inventors (TRI) and to incubate the Multi Business Model (MBM). The motivation behind the GCELII is,
“Innovation needs courage: courage to think differently, courage to invent, courage to discover the impossible, courage to combat the problems and succeed.” – By Dr. A.P.J Abdul Kalam.
iii) Preamble
GCET is dedicated to working towards the promotion of entrepreneurship among the students. We work to establish a startup ecosystem and provide young entrepreneurs a platform to work out on their ideas and motivate them for this adventurous journey of building a startup from scratch. The students are motivated to take benefits from the different initiatives launched by the government of India such as Startup India, Make in India, Digital India, Smart Cities, etc. and contribute effectively in nation building. We invite various eminent entrepreneurs to deliver lectures and educate students about the joys and hardships of entrepreneurship. They share the knowledge for idea implementation and funding resources. Our aim is to bring the innovative ideas out of the young minds of our college and nearby to help them with it. With a long felt need for streamlining the growth in innovative ventures of the students and their interest in entrepreneurial endeavors as a career option, a Innovation and Entrepreneurship council has been established under the chair of Dean, Innovation and Incubation with a separate IEC policy in 2021. The policy primarily focused on guiding the functioning IEC. With the release of national Innovation and Startup Policy for students and faculty (NISP) in 2019, Galgotias educational institution has compiled and aligned its own policy which is presented in following lines.
The Institute follows the following step-wise approach in its year-long activities to achieve the mission mentioned above:
- Generating awareness about entrepreneurship and the benefits of start-ups.
- Developing and fostering entrepreneurial attitudes.
- Building the support mechanisms that give momentum to the entrepreneurial spirit
iv) Vision
“To become a world-class technology driven incubator and provide a universal platform for research and development for the benefits of budding entrepreneurs, corporate houses & the society at large”.
Mission
“To develop an innovative ecosystem powered by experiential learning and foster a business model based on the latest technology, having innovation and scalability as an essential component with the highest profit and lowest risk”.
Short term Objectives
- To establish a laboratory for budding techno-management students to learn, experiment and test their innovative business ideas which could be commercialized.
- To foster an environment where a sense of creativity, originality and capacity to transform innovative skills & business ideas could be inculcated.
- To provide enabling mechanisms to start-ups, through training and skill development, capacity building, networking, access to knowledge & support services, etc. on a continuous basis.
- To provide the guidelines to stakeholders of GCET for developing entrepreneurial agenda, managing Intellectual Property Rights (IPR) ownership, technology licensing and equity sharing in Startups or enterprises established by faculty and students.
Long Term Objectives
To improve the quality of research works of students and turn their ideas into revenue-based models.
- To nurture and produce a pool of proficient entrepreneurs in the society.
- To participate and contribute in the Government's initiative for self-employment.
- To contribute towards the success of the ‘Make in India’ campaign, according to which there will be 100 million additional manufacturing jobs in coming years.
- To provide a platform for students to develop innovative products with global recognition and generate business opportunities.
1. Strategies and Governance
Strategies and Governance is an essential element of business success - especially in early-stage startups. Newborn companies are usually in the most in need of the support structure that a small, fit-for-purpose board provides. Following steps have been taken to implement IEC policy.
- Experiential Learning based Innovation and Incubation center has been established to facilitate development of an entrepreneurial ecosystem in the organization with specific objectives.
- A minimum of one percent in the total annual budget of the Institution has to be allocated to support and fund the new innovation and start-up related work with the establishment of a dedicated Institutions’ Innovation Council which handles the Innovation funds for promoting Innovation & Entrepreneurship (I&E) shall be encouraged.
- Encouragement shall be given for raising funds through sponsorships and donations engaging alumni network and external sources government (state and central) such as DST, DBT, MHRD, AICTE, TDB, TIFAC, DSIR, CSIR, NRDC, Startup India, Invest India, MeitY, MSDE, MSME, startup in UP as well as non-government sources to reduce dependency on the public funding.
- Innovation Center under IEC will organize institutional programs such as conferences, convocations, workshops etc. to spread the awareness regarding importance of innovation and entrepreneurial agenda across the institute.
- Product to market strategy for startups which is a part of IEC policy document will be finalized on micro level on a case to case basis.
- Efforts will be encouraged to make GCET as a driving force in developing entrepreneurship culture in its vicinity (regional, social and community level). These efforts include giving opportunity for regional startups, provision to extend facilities for outsiders and active involvement of GCET in defining strategic direction for local development.
- GCET has initiated the setup of student owned E-Cell to propagate and involve the student community to take enterprising activities Viz. awareness, HULT prize, Hackathon etc.
2. Startups Enabling Institutional Infrastructure
Institute has already developed institutional infrastructure to enable startups and progressed in this direction from innovation Cell. As a part of developed infrastructure, two dedicated centers named Center for Experiential Learning and Nano Tech Enabled Multidisciplinary Center and has been established in B-block. It comprises of all the facilities of prototyping, mentoring for IPR, marketing, business plan development, product development etc.
Under developing experimental setup for experiential learning:
- “Drone Development for Different applications: DD for DA”
- “Self-Driving Vehicle Development for Future Applications: SDVD for FA”
- “Nano-Satellite Development for Versatile Applications: NSD for VA ”
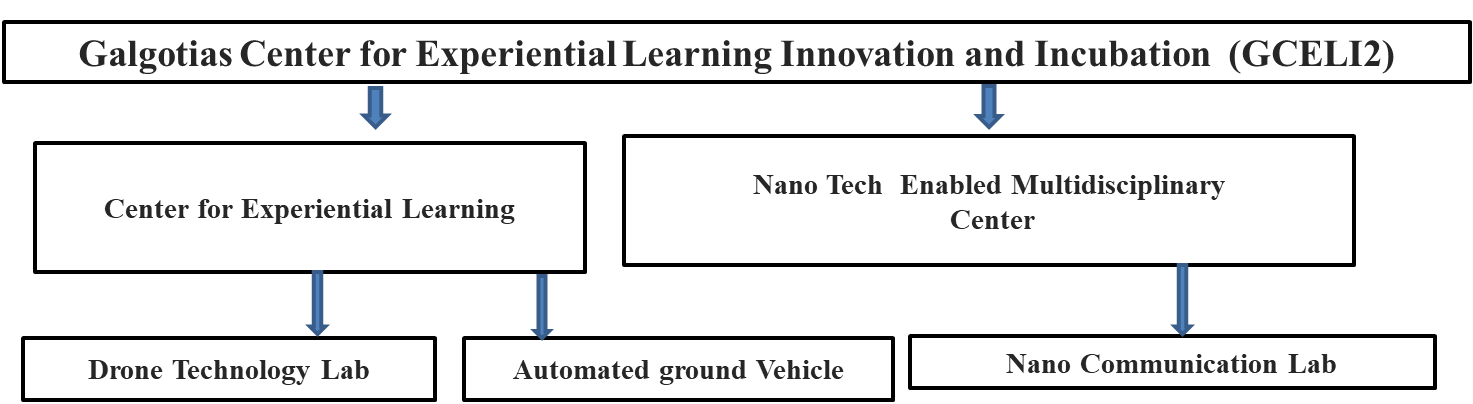
Figure 1: Structure for Innovation cell
Thus, creation of pre-incubation and incubation facilities for nurturing innovations and startups in GCET has already taken place under Galgotias Centre for Experiential Learning, Innovation and Incubation (GCELII) and IEC policy document reflects the roadmap of innovation to enterprises to financial success. A functional IIC is managing all the activities regarding innovation, entrepreneurship and startup related activities within the institute.
3. Nurturing Innovations and Startups
For easy creation and nurturing of Startups/enterprises applicants may be students (UG, PG), staff (including temporary or project staff), faculty, alumni and potential start up applicants even from outside the institutions. The preference will be given to those startups which are useful in rural development, helpful in transforming life of the people and which have potential to sustain in the market. Institute will facilitate the startup activities/ technology development by allowing students/faculty/ staff to use institute infrastructure and facilities, as per the choice of the potential entrepreneur in the following manners:
- Mentorship support on a regular basis.
- Facilitation in a variety of areas including technology development, ideation, creativity, design thinking, fund raising, financial management, cash-flow management, new venture planning, business development, product development, social entrepreneurship, product-costing, marketing, brand-development, human resource management as well as law and regulations impacting a business.
- Institute may also link the startups to the seed-fund provider/angel funds/venture funds or itself may set up seed-fund once the incubation activities mature.
- In return for the services and facilities, the institute may take 2% to 9.5% equity/ stake in the startup/ company, based on brand use, faculty contribution, support provided and use of the institute's IPR (According to NISP policy 2019)
- For staff and faculty, institutes can take no more than 20% of shares that staff/faculty takes while drawing full salary from the institution; however, this share will be within the 9.5% cap of company shares, listed above.
- No restriction on shares that faculty/staff can take, as long as they don’t spend more than 20% of office time on the startup in advisory or consultative roles and do not compromise with their existing academic and administrative work/duties. In case the faculty/staff holds the executive or managerial position for more than three months in a startup, then they will go on sabbatical/leave without pay/ earned leave.
- Product development and commercialization as well as participating and nurturing of startups would now be added to a bucket of faculty-duties and each faculty would choose a mix and match of these activities (in addition to minimum required teaching and guidance) and then respective faculty are evaluated accordingly for their performance and promotion.
- Institute could extend this startup facility to alumni of the institute as well as outsiders. Participation in startup related activities needs to be considered as a legitimate activity of faculty in addition to teaching, R&D projects, industrial consultancy and management duties and must be considered while evaluating the annual performance of the faculty. Every faculty may have the courage to mentor at least one startup.
- Institutions might also need to update/change/revise performance evaluation policies for faculty and staff as stated above.
- License institute IPR as discussed in the next section.
4. IP and Product Ownership Rights for Technologies Developed at Institute
A separate IPR policy is in place for addressing the guidelines and issues regarding Product Ownership Rights for Technologies Developed at Institute. Students who are developing and demonstrating proof of concepts of their ideas in minor and major project exhibitions, inter-institute competitions, hackathons etc. are facilitated in Galgotias Centre for Experiential Learning, Innovation and Incubation (GCELII) and further provide platform to convert their PoCs into MVPs.
5. Organizational Capacity, Human Resources and Incentives
Organizational Structure for Innovation and Entrepreneurship is shown in figure 1. IEC policy document is available regarding implementation of all Innovation and Entrepreneurship related activities and programs.
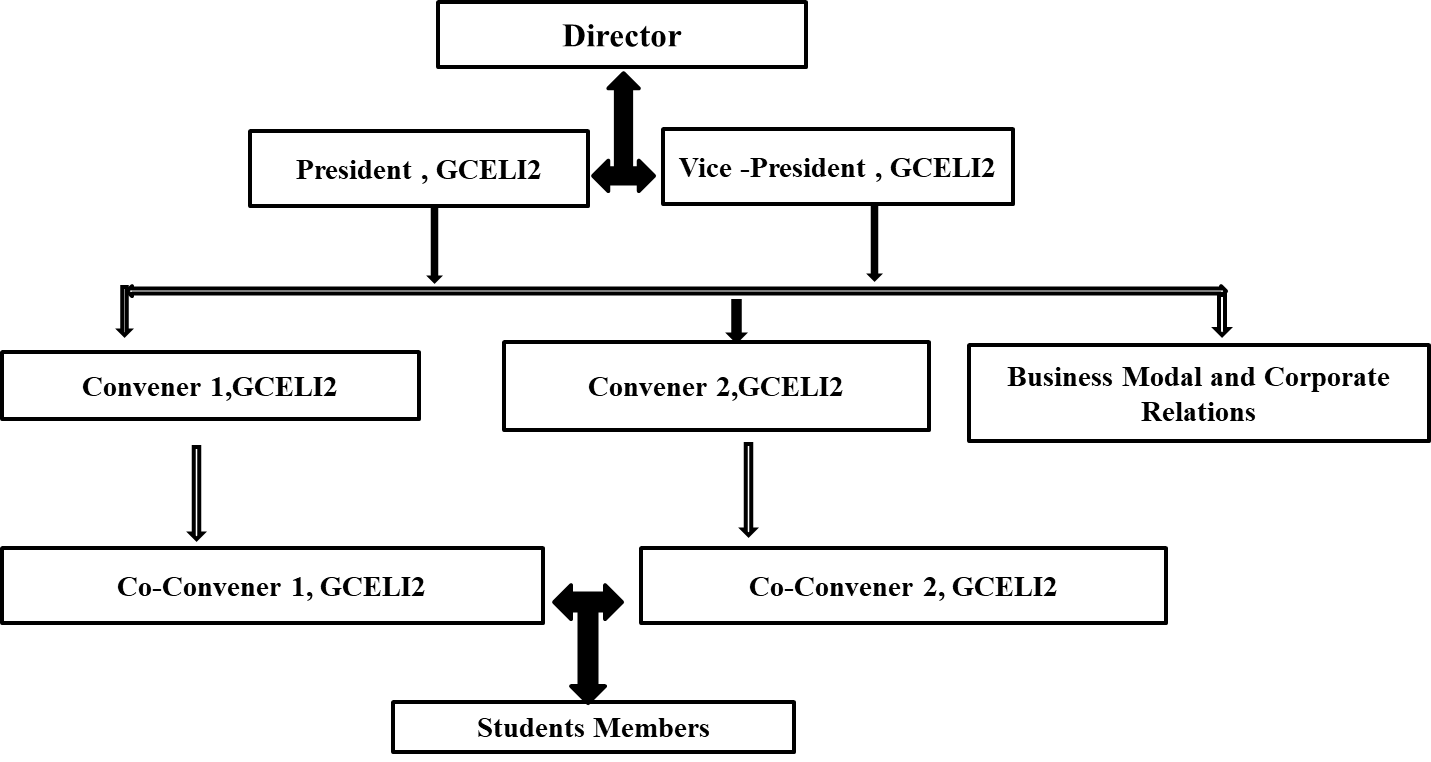
Figure 2: Organizational Structure for Innovation and Entrepreneurship.
6. Creating Innovation Pipeline and Pathways for Entrepreneurs at Institute Level
To ensure exposure of maximum students to innovation and pre-incubation activities at their early stage and to support the pathway from ideation to innovation to market, mechanisms should be crafted at institution level through various steps.
- The awareness programs conducted by Galgotias Centre for Experiential Learning, Innovation and Incubation (GCELII) under their structured Entrepreneurship Awareness Camps/session, expert talk conducted during induction programs for first year students.
- Specialized workshops and short-term courses in IPR, entrepreneurship development, various technology-based skill development programs etc. help students to develop various skills required in their entrepreneurial journey. The Innovation Pipeline and Pathways for Entrepreneurs at Institute Level is shown in figure 3.
- The institute should establish Institution’s Innovation Councils (IICs) as per the guidelines of MHRD’s Innovation Cell and allocate appropriate budget for its activities. IICs should guide institutions in conducting various activities related to innovation, startup and entrepreneurship development. The collective and concentrated efforts should be undertaken to identify, scout, acknowledge, and support innovative ideas and further facilitate their entrepreneurial journey.
- To strengthen the innovation channel of the institute, access to financing must be opened for the potential entrepreneurs.
- Provide business incubation facilities: premises at subsidized cost. Laboratories, research facilities, IT services, training, mentoring, etc. should be accessible to the new startups.
- Networking events must be organized to create a platform for the budding entrepreneurs to meet investors and pitch their ideas.
- A culture needs to be promoted to understand that money is risk capital. The entrepreneur must utilize these funds and return. While funding is taking a risk on the entrepreneur, it is an obligation of the entrepreneur to make every effort possible to prove that the funding agency did the right thing in funding him/her.
- We have specific committees for selection for incubation and project monitoring committees in GCELII consisting of experts from incubation and entrepreneurship, prototype development, IPR, marketing, finance and technology experts. Students who have exhibited interest in entrepreneurship and innovation by participating and mentoring for business plan development and idea pitching for incubation in GCELII.
- The students incubated in GCELII must present their proposal in front of the Project Selection Committee for funding through various government schemes and agencies.
- For rapid prototyping or product development facilities are being provided by GCELII through Innovation Center known as
- Center for experiential learning comprising the latest Drone technology and advanced automated vehicles.
- Nano Tech Enabled Multidisciplinary Center
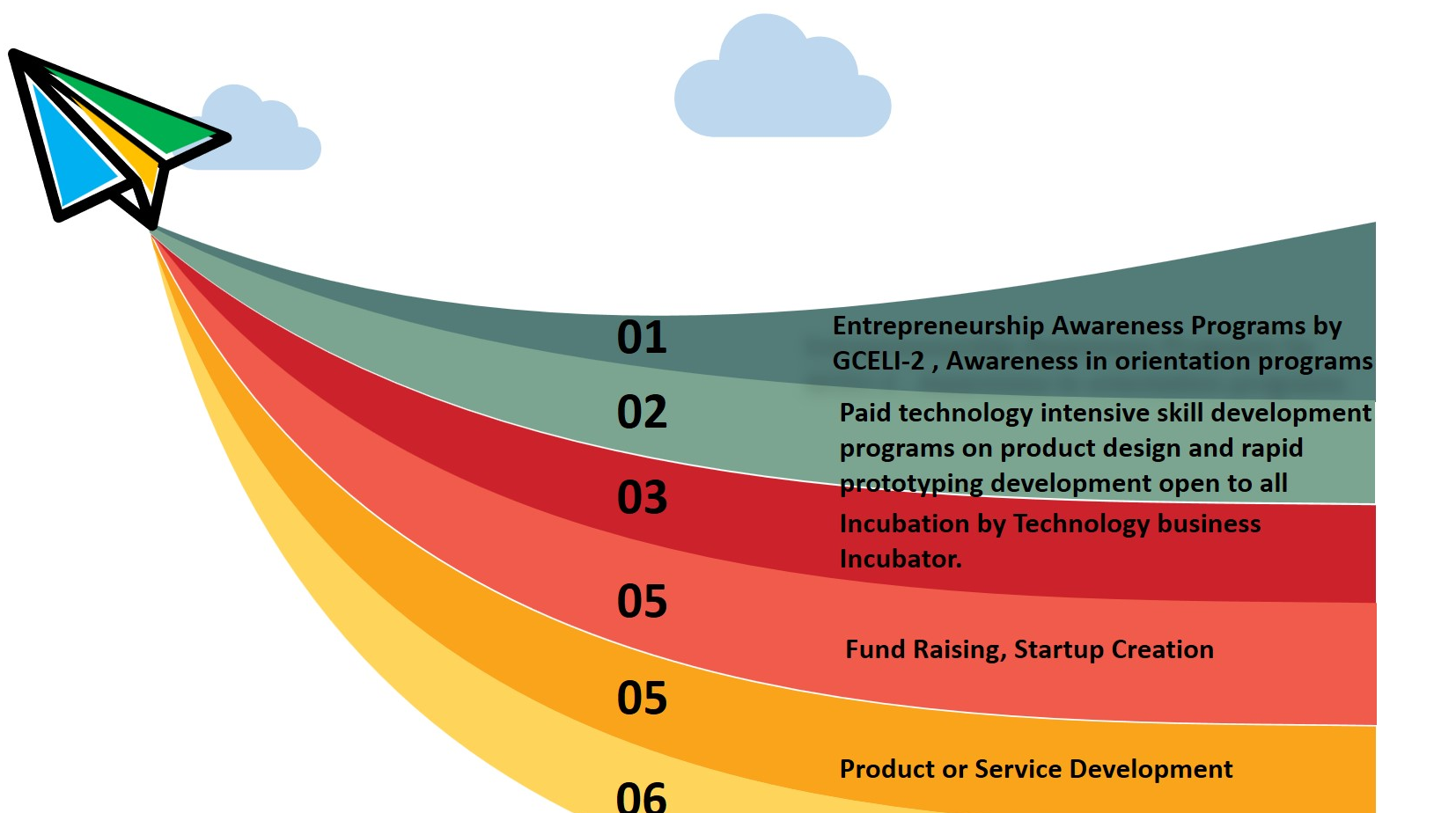
Figure3: Innovation Pipeline and Pathways for Entrepreneurs at Institute Level
When an incubated student registers his/her company, he/she is mentored and introduced to angel investors, venture capitalists and investors for scaling up his/ her business.
7. Norms for Faculty Startups
Norms for Faculty to initiate/promote innovation and startup activity is a crucial parameter, and it should be created by the institutes.
- Role of faculty may vary from being an owner/ direct promoter, mentor, consultant or as on-board member of the startup.
- Only those technologies should be taken for faculty startups which originate from within the same institute.
- Institutes should work on developing a policy on 'conflict of Interests' to ensure that the regular duties of the faculty don’t suffer owing to his/her involvement in the startup activities.
- Faculty startup may consist of faculty members alone or with students or with faculty of other institutes or with alumni or with other entrepreneurs.
- Faculty must clearly separate and distinguish on-going research at the institute from the work conducted at the startup/company.
- In case of selection of a faculty startup by an outside national or international accelerator, a maximum leave (as sabbatical/ existing leave/ unpaid leave/ casual leave/ earned leave) of one semester/ year (or even more depending upon the decision of review committee constituted by the institute) may be permitted to the faculty.
- Faculty must not accept gifts from the startup.
- Faculty must not involve research staff or other staff of the Institute in activities at the Startup and vica- versa.
- Human subject related research in Startup should get clearance from the ethics committee of this Institution.
8. Pedagogy and Learning Interventions for Entrepreneurship Development
A diversified approach in teaching and learning pedagogy including cross disciplinary learning using mentors, labs, case studies, games, etc. in place of traditional lecture-based delivery. A dedicated innovation center is responsible for coordinating all student clubs, whereas individual departments are responsible for running technical hobby clubs, project workshops/labs.
- GCELII is responsible for organizing competitions, boot- camps, workshops, awards, etc., which is totally involved students in strategic planning and implementation of these activities.
- As a part of awareness program about the entrepreneurial ecosystem present in the institute, introductory sessions will be organized for students at institute level. The required slots will be allocated in the timetable of every department in coordination with the Dean, GCELII. The learning journey of an aspiring entrepreneur is shown in figure 4.
- To promote student ideas, projects and innovations based around real life challenges, boot-camps, visits to rural and underprivileged areas in nearby region and hackathons will be organized by Galgotias Centre for Experiential Learning, Innovation and Incubation (GCELII) on regular basis. These activities and other IIC calendar activities will be displayed in the institute’s activity calendar.
- Innovation champions should be nominated from within the students/ faculty/ staff for each department/stream of study.
- Institute recognizes outstanding ideas, successful enterprises and contributors for promoting innovation and the enterprise ecosystem within the institute and facilitates through award.
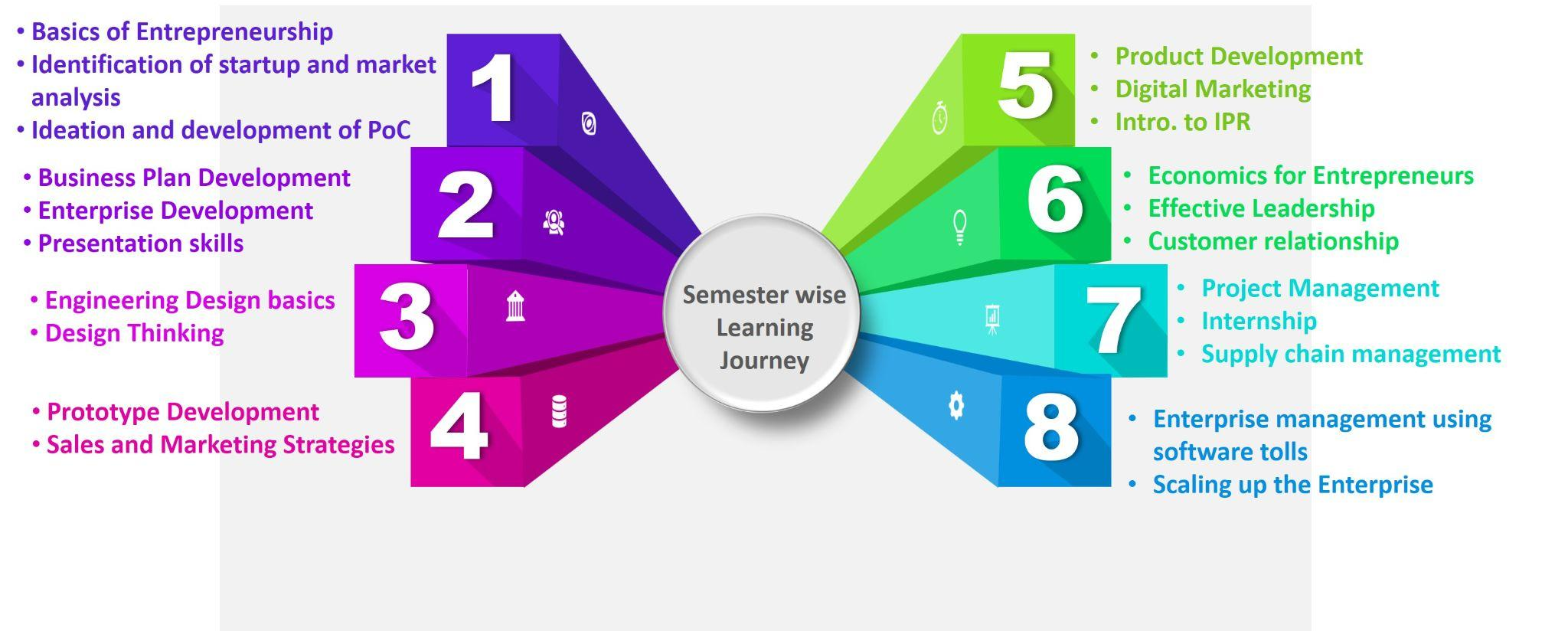
Figure 4. The learning journey of aspirant entrepreneurs
9. Collaboration, Co-creation, Business Relationships and Knowledge Exchange
Co-creation unlocks new perspectives through building community and teams provide open collaboration and participation. It play important role in increases idea,generate opportunity, which relatively reduces the costs and risks associated with development
- For all the activities relevant to the entrepreneurial agenda of the institute, participation and collaboration of industry partners, institutes of national importance, international institutions, social enterprises, schools, alumni, professional bodies and entrepreneurs will be encouraged.
- Dean IEC and his team will be Single Point of Contact (SPOC) in the institute for the students, faculty, collaborators, partners and other stakeholders.
- Institute has collaborations with associations of industries IIA, CII, CEL etc., with various government departments and ministries like DST, MeitY, UPIT, Govt. of UP etc, ITI and poly-technique institutes, research organizations like NRDC, entrepreneurship promoting institutes EDII, and international organizations like INNOPICs, IP firms and network of angel funding and venture capitalists etc. All these collaborations prove to be beneficial to the students in their entrepreneurial journey.
10. Entrepreneurial Impact Assessment
Well-defined evaluation parameters are formulated to assess the impact of various stages of entrepreneurial development such as entrepreneurship education, pre-incubation, incubation etc. This entrepreneurial assessment is performed through the monitoring and evaluation of the knowledge exchange initiatives and exchange of all departments and faculty in the entrepreneurial teaching and learning. Also, the various support systems created, new business relationships established in the institute have to be recorded. These records and key performance indicators are used for the Entrepreneurial Impact assessment. The key parameters are listed below for assessment of growth and development in startup and entrepreneurship activities.
- Satisfaction of the participants in micro degree certification program, workshops and training programs.
- Participation in awareness programs.
- Utilization of pre-incubation facilities by students.
- Number of curriculum projects addressing real life problems.
- Participation in various ideas, PoC, Prototype, b-plan competitions and hackathons.
- Participation in pitching for fundraising and grants/support from government and non-government agencies.
- Contribution in industrial projects and consultancy projects.
- Idea to PoC projects.
- PoC to Prototype/MVP projects.
- Product development and its launching in the market.
- Fund raising.
- Startup registrations and company incorporation.
- Annual Turn over
- IPR application filing, grant and commercialization
The IEC team in chairmanship of Dean, Galgotias Centre for Experiential Learning, Innovation and Incubation (GCELII) will be responsible for assigning appropriate weightages to the above parameters depending on the maturity of the process. A separate document regarding this will be made available by IIC and reviewed annually.
11. Review of the Policy
Considering the feedback from the assessment team which is the reflection of impact of the existing policy, Dean IEC, Galgotias Centre for Experiential Learning, Innovation and Incubation (GCELII) shall organize the review committee meeting and finalize the recommendations of the review committee. NISP Implementation Committee has been formed to identify the experts having expertise and experience in the domain of innovation, IPR, and startup to start the work of policy formulation and implementation of guidelines at the institute.
12. Way Forward
Successful implementation of the Innovation and Startup Policy, GCET (ISP-GCET) for students and faculty is the main objective. To achieve this, full-fledged support of all the academic, non -academic and supporting departments will be important. The roadmap suggested through this document is ‘broad guidelines’ and this policy document is supported by previously existing policy documents on innovation and entrepreneurship council, IPR, Industry-Institute interaction and research and development.